What is the difference between phishing and spear-phishing?
Phishing and spear-phishing are both forms of cybercrime in which victims are tricked into giving away sensitive data. While both have similarities, there are a few notable distinctions between the two types of attacks.
Article Contents
Here are the official definitions of phishing & spear phishing from Oxford Languages:
Phishing:
- The fraudulent practice of sending emails purporting to be from reputable companies induces individuals to reveal personal information, such as passwords and credit card numbers. – “an email that is likely a phishing scam.”
Spear phishing:
- The fraudulent practice of sending emails ostensibly from a known or trusted sender to induce targeted individuals to reveal confidential information. – “spear-phishing represents a serious threat for every industry.”
Spear-phishing is a targeted attack aimed at specific individuals, and phishing is a non-targeted attack typically executed by sending millions of spam emails.
Phishing attacks are easier to detect, as they typically use more generic emails and are sent to large numbers of people. In contrast, spear-phishing is more dangerous because it focuses on an individual with personalized information.
What is phishing, and how do I spot it?
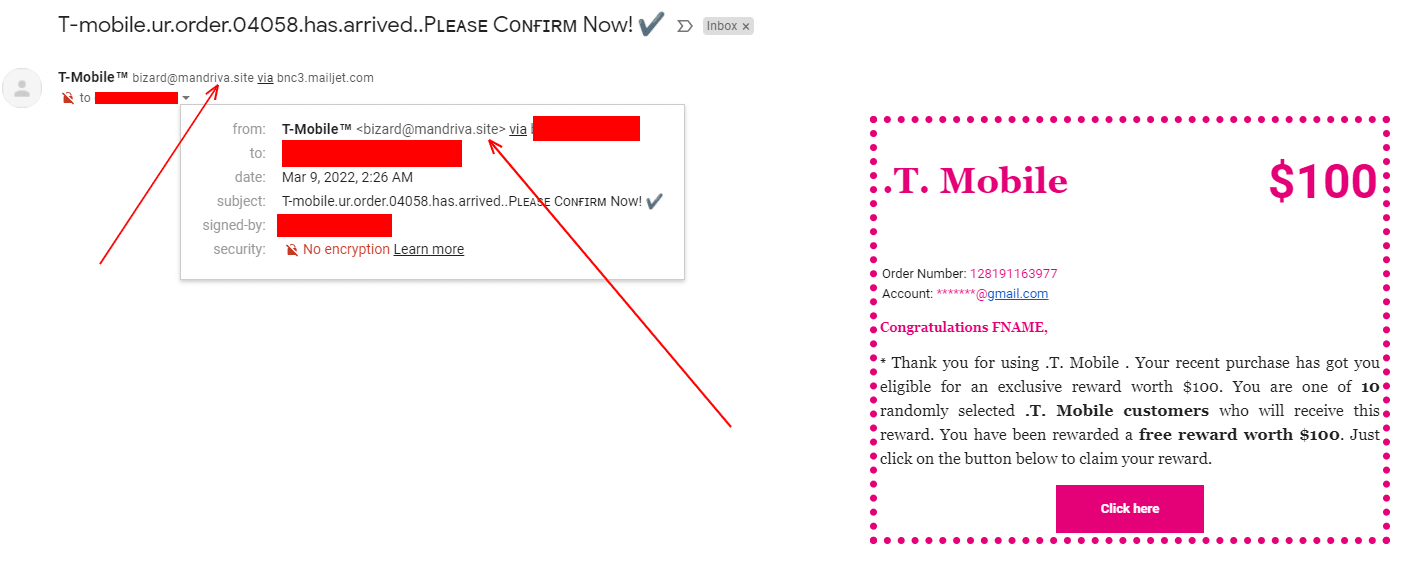
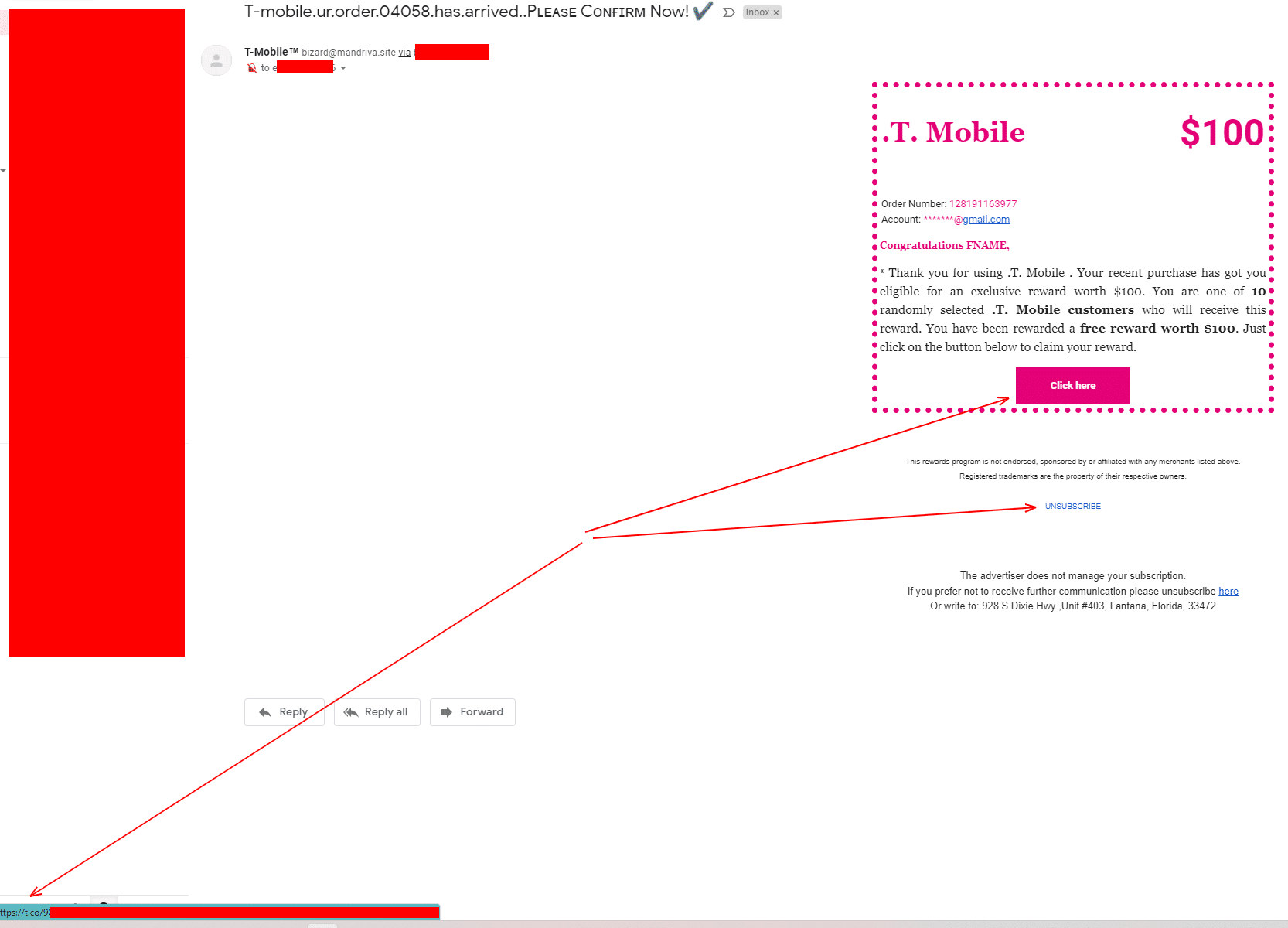
Examples of phishing emails:
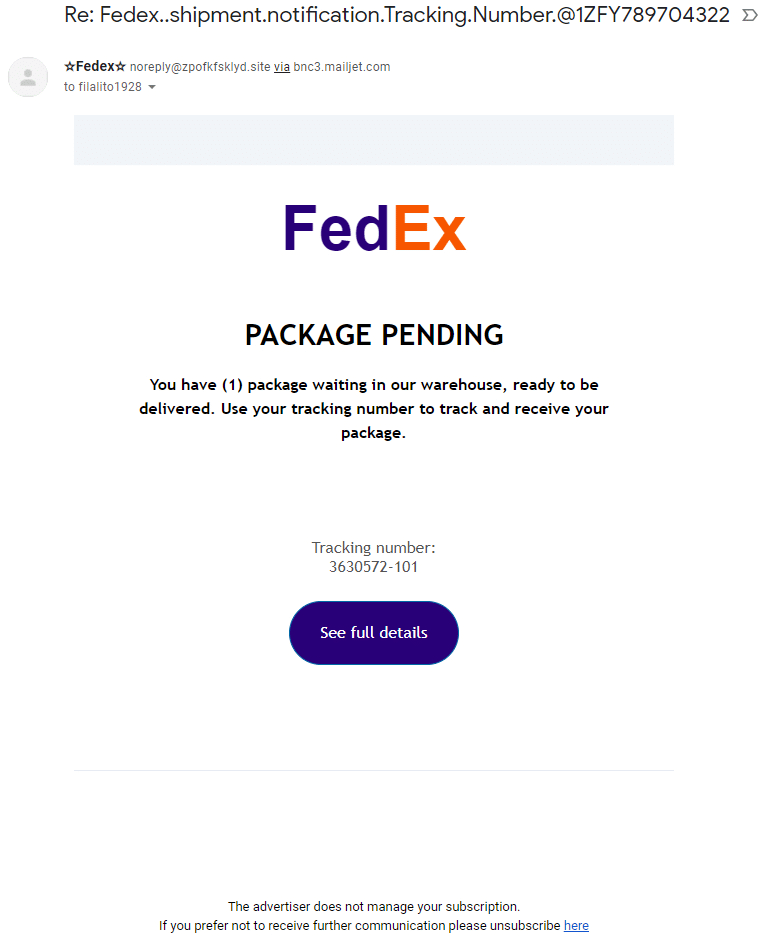
As you can see in the above screenshot, we received an email reporting to be from FedEx that we have a package waiting in a warehouse. The phishing scam here wants us to click on the link ‘See Full Details.’
How to quickly identify this phish
Nerds On Site recommends looking at two core pieces of information before taking action on any email. These actions take about 5 seconds and will potentially save you and your organization hundreds of thousands of dollars in remediation costs.
Check the email address where it originated.
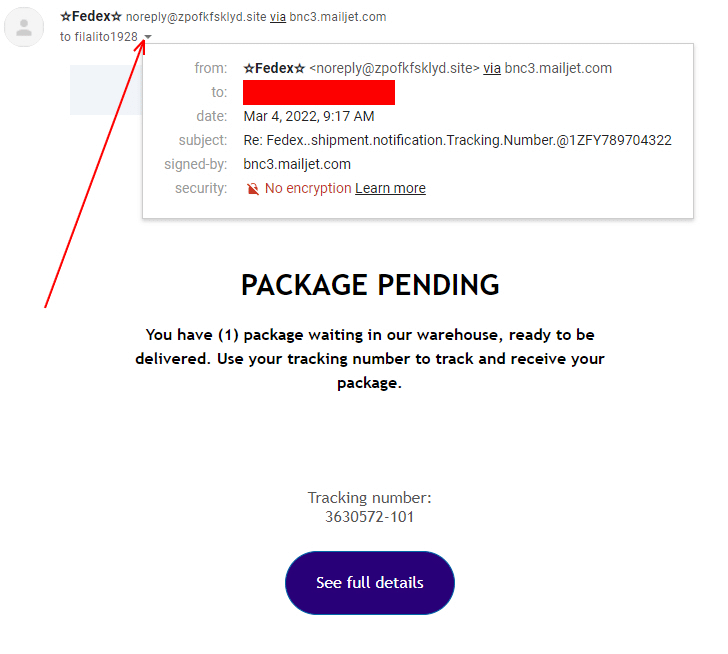
As you can see in the above example, this email came from zpofkfsklyd.site. FedEx, or any other company, will never email you from a non-corporate web address.
Phishers can get trickier by making domains similar to the company they are trying to fake. In this case, you have to pay extra attention. An example would be that FedEx would send you emails from fedex.com, not FedEx-tracking.com.
Check where the links are trying to take you.
In this particular case, this email has two separate links. Let’s see where they go.
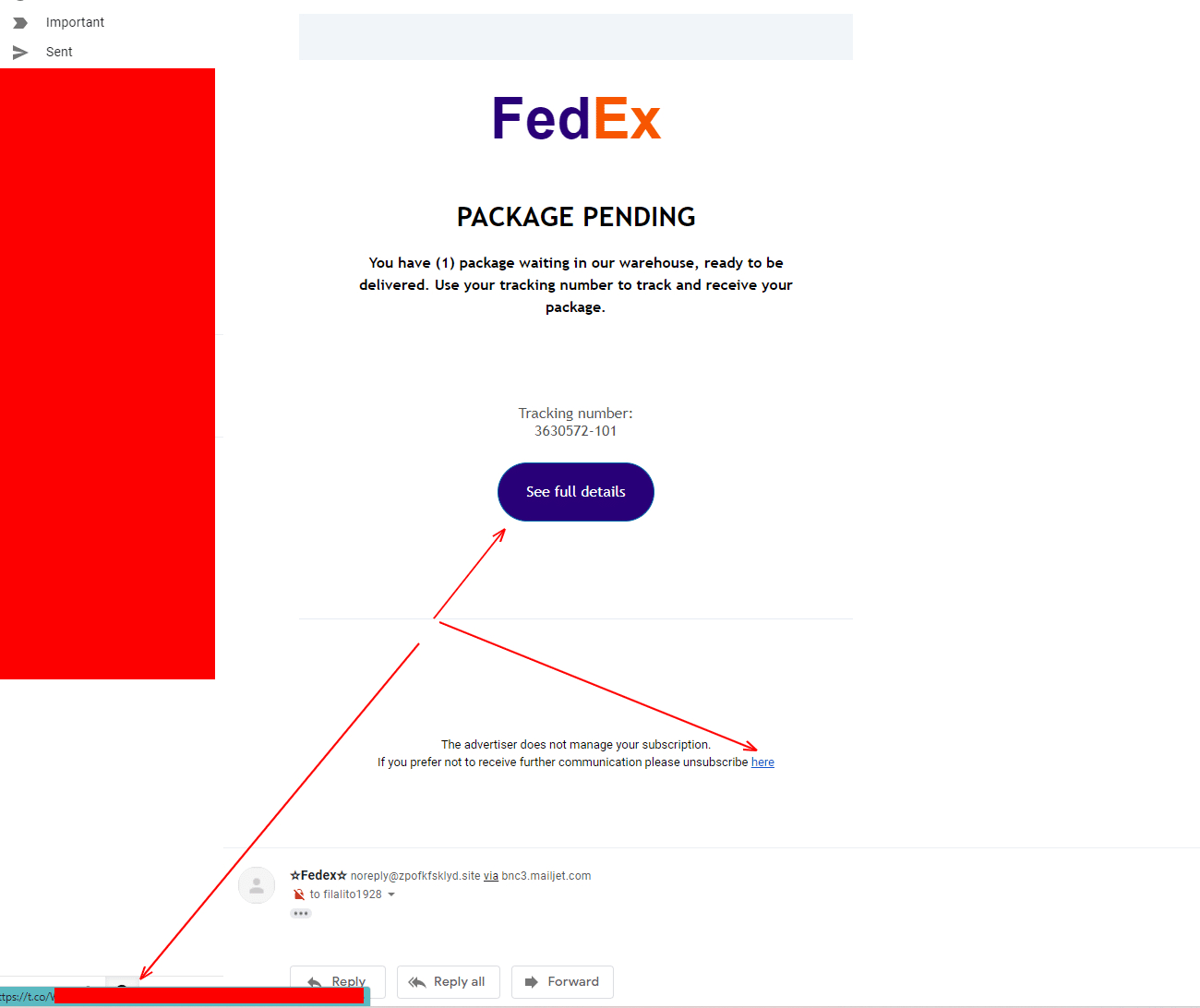
By hovering our mouse over the links (See Full Details & here), we can see (in the bottom left corner of the screen) they both go to the same t.co address. T.co is twitters web address shortening service and not something that a large company would include in their emails.
If it isn’t a direct link to the company’s website, using its corporate web address, it’s likely a phishing scam, and caution should be taken.
Does it make sense?
While I order items delivered by FedEx, I wasn’t expecting anything from them at that particular time, so it’s doubtful a parcel would have been waiting for me.
What if it does make sense?
Simple! Don’t use the email! Go directly to the company website or call the company’s customer service and enquire now.
Another Example
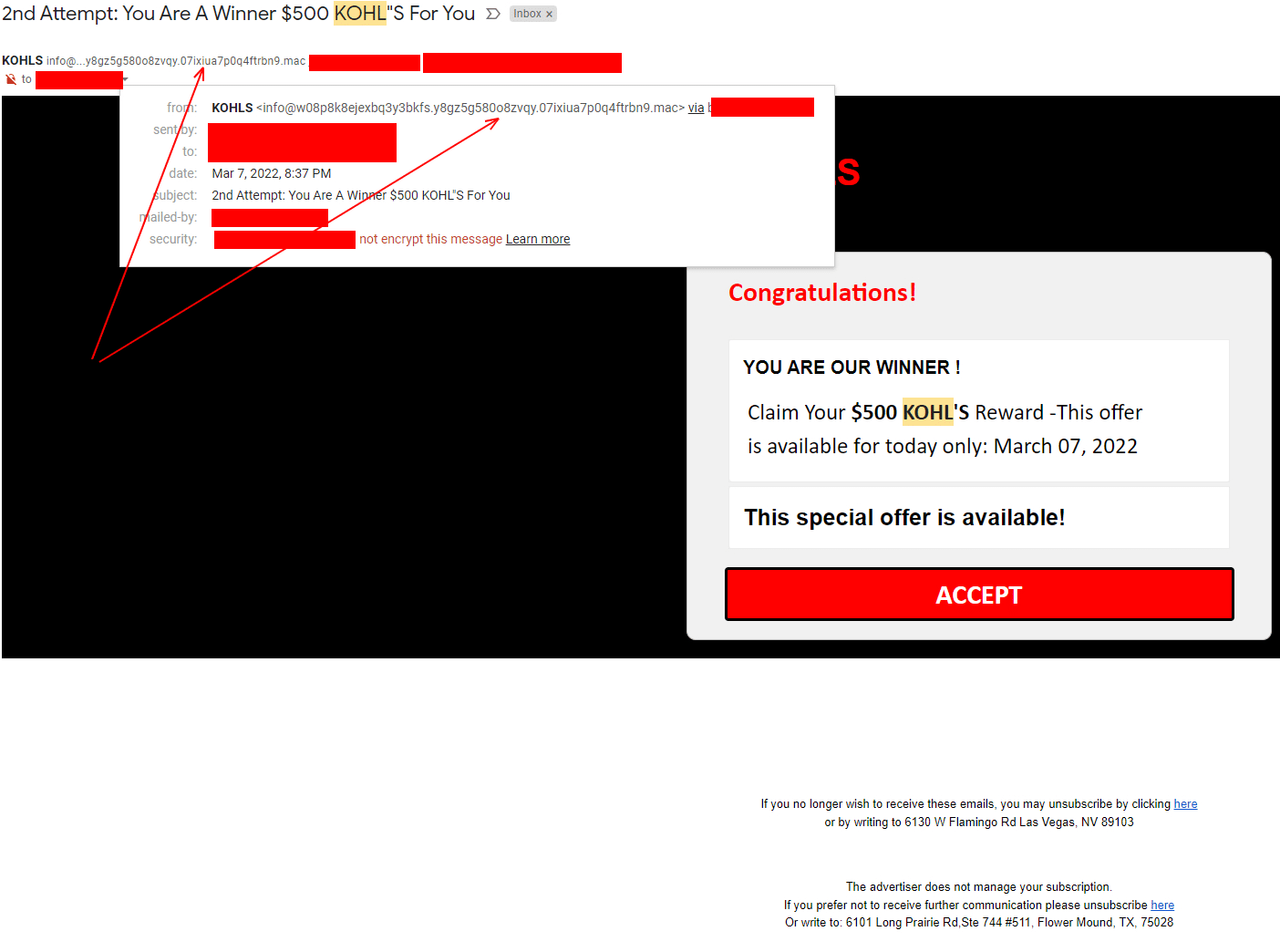
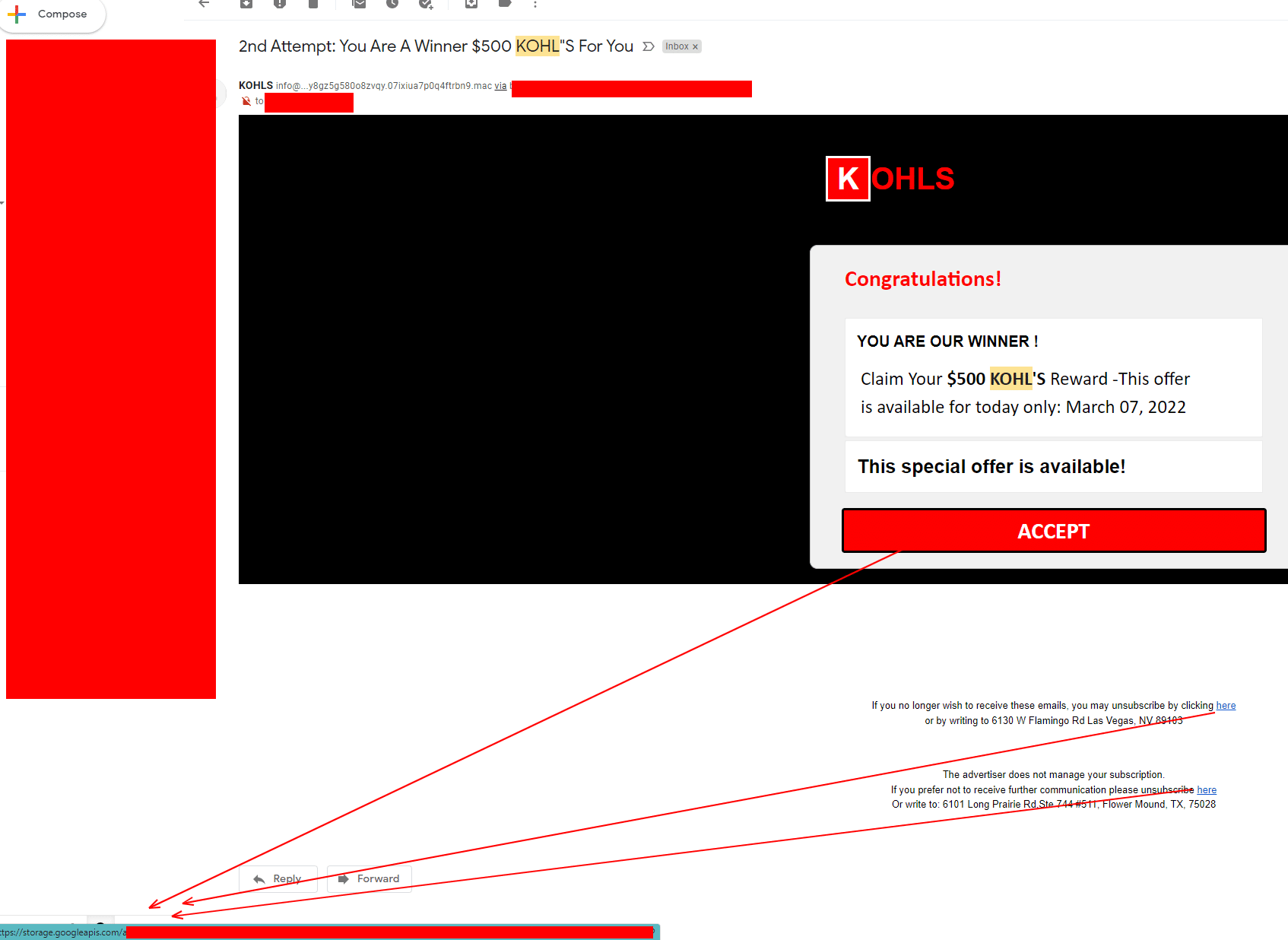
As you can see above, all three of these examples can be easily identified and ignored by simply checking the email address and checking where the links are trying to take us.
What is spear-phishing, and how do I spot it?
Spear-phishing, also known as Business Email Compromise (BEC), is much more dangerous and, in some cases, much more challenging to spot.
A Spear-phishing attack is a focused phishing campaign that aims at a specific individual and usually contains information known to be of interest to the targeted individual, such as financial or business documents.
High-profile spear phishing attacks
Facebook & Google
The first example I’m going to share is from two of the biggest companies in the world, for ridiculous amounts of money. While the companies involved lost money, the attacker, Evaldas Rimasauskas, was sentenced to five years in prison in 2019.
Evaldas set up a company called Quanta Computer, the same name as a known hardware supplier for both Facebook & Google. They sent in invoices to the accounts payable department from 2013-2015. During this time, Evaldas could fraudulently claim around $121,000,000 (121 Million USD!).
Had the accounts payable department looked at the originating email/domain; this could have been avoided.
Ubiquiti
According to Ubiquiti’s Securities & Exchange Commission (SEC) filing in August 2015, the company fell victim to a $46,000,000 (46 Million USD!) business fraud. Details on this event aren’t entirely known, but we know it was a similar event as above, where spear-phishers could claim invoices via the accounts payable department.
Toyota
In 2019 Toyota was a victim to a $37,000,000 (37 Million USD!) spear-phishing campaign that convinced an employee to send the money from a European subsidiary.
Stories are great, but how do they help me?
It’s highly probable that if the employees involved in the above scams had known the correct web addresses and email addresses of the organizations they were paying, along with enough training to identify these spear-phishing campaigns, they would have never lost the money.
When the advice here breaks down
We weren’t giving you the whole picture! Sometimes, our advice doesn’t help. Sometimes you cannot tell. Sometimes it looks like an EMAIL IS COMING FROM THE RIGHT PLACE/PERSON!
Without getting too technical, there are email & web settings that companies need to configure to secure their email manually. If these settings are not done correctly by a professional, cyber criminals can send emails from your web address within your organization or to the outside.
Example:
I setup nerdsonsite.com
I do not secure nerdsonsite.com web & email settings (it is secure 🙂
Any knowledgeable cyber criminal will now be able to send emails from ANY EMAIL @nerdsonsite.com.
These are DMARC, DKIM & SPF settings.
How do I set DMARC, DKIM & SPF settings for my organization?
You can check using MX Toolbox as to whether they are configured correctly, but if they are not, we recommend contacting a professional.
How can spear-phishing be prevented?
Spear-phishing emails are designed to trick victims into taking actions that hurt them or their organization. To defend against spear-phishing campaigns, organizations should provide security awareness training to help employees and managers identify, avoid, and report fraudulent emails.
Every employee should recognize their role and responsibilities in preventing spear-phishing attacks, the importance of email security, and the urgency behind protecting sensitive information. Here are some common-sense preventative measures to help protect your organization from phishing attacks:
Provide security awareness training
Security awareness training is a process of educating employees about cybercrime, including phishing and spear-phishing. Security awareness training helps employees learn how to identify and avoid potential attacks. Additionally, security awareness training helps employees understand the importance of protecting sensitive data and how to report any suspicious activity.
Ensure your organization uses Multifactor Authentication (MFA).
Multifactor authentication is a security process that requires more than one type of authentication to verify the user’s identity. For instance, multi-factor authentication can be a combination of factors such as something the user knows (a password), something the user has (a security token), and something the user is (biometric data).
The interactive process makes it more difficult for spear-phishers to gain access to accounts if they do manage to obtain credentials.
It’s worth noting that when we say MFA, we are not talking about 2 Factor Authentication (2FA). 2FA often involves email or text verification. It’s straightforward for cyber criminals to “Sim Swap” your number and even easier for them to access your email if your credentials have already been exposed.
Use anti-phishing software.
Anti-phishing software such as the Nerds On Site SME Edge is designed to protect users from fraudulent emails, aka phishing attacks. The SME Edge can help users identify phishing emails, links, and websites, preventing the loss of sensitive data.
Phishing and Spear-Phishing Summarized
Phishing and spear-phishing attacks are severe threats to your employees and the organization’s computer system security. Understanding these attacks can better protect you and your employees from becoming victims.
Want to know more about phishing, spear-phishing, or cyber security?
Have you been a victim of a targeted phishing attack and require a solution? Or, are you simply interested in learning more about cyber security, contact us.